The world’s top-performing system for graph processing at scale was constructed on a commercially obtainable cluster.
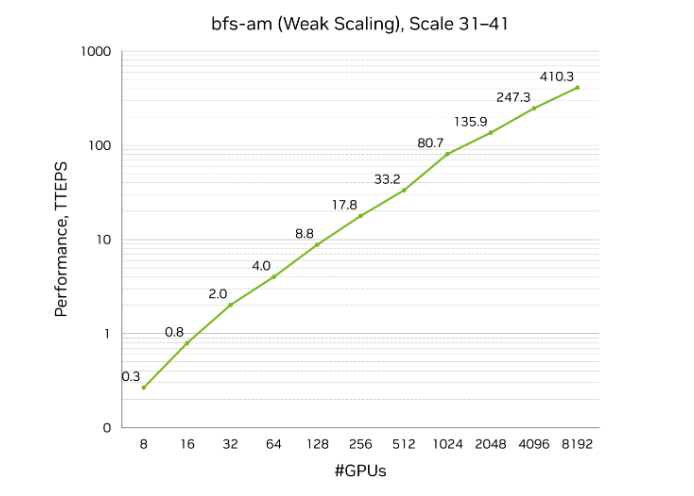
NVIDIA final month introduced a record-breaking benchmark results of 410 trillion traversed edges per second (TEPS), rating No. 1 on the thirty first Graph500 breadth-first search (BFS) listing.
Carried out on an accelerated computing cluster hosted in a CoreWeave information heart in Dallas, the profitable run used 8,192 NVIDIA H100 GPUs to course of a graph with 2.2 trillion vertices and 35 trillion edges. This result’s greater than double the efficiency of comparable options on the listing, together with these hosted in nationwide labs.
To place this efficiency in perspective, say each particular person on Earth has 150 associates. This could signify 1.2 trillion edges in a graph of social relationships. The extent of efficiency not too long ago achieved by NVIDIA and CoreWeave permits looking via each good friend relationship on Earth in nearly three milliseconds.
Velocity at that scale is half the story — the true breakthrough is effectivity. A comparable entry within the prime 10 runs of the Graph500 listing used about 9,000 nodes, whereas the profitable run from NVIDIA used simply over 1,000 nodes, delivering 3x higher efficiency per greenback.
NVIDIA tapped into the mixed energy of its full-stack compute, networking and software program applied sciences — together with the NVIDIA CUDA platform, Spectrum-X networking, H100 GPUs and a brand new lively messaging library — to push the boundaries of efficiency whereas minimizing {hardware} footprint.
By saving vital time and prices at this scale in a commercially obtainable system, the win demonstrates how the NVIDIA computing platform is able to democratize entry to acceleration of the world’s largest sparse, irregular workloads — involving information and work objects that are available in various and unpredictable sizes — along with dense workloads like AI coaching.
How Graphs at Scale Work
Graphs are the underlying data construction for contemporary expertise. Individuals work together with them on social networks and banking apps, amongst different use instances, every single day. Graphs seize relationships between items of data in large webs of data.
For instance, contemplate LinkedIn. A person’s profile is a vertex. Connections or relationships to different customers are edges — with different customers represented as vertices. Some customers have 5 connections, others have 50,000. This creates variable density throughout the graph, making it sparse and irregular. In contrast to a picture or language mannequin, which is structured and dense, a graph is unpredictable.
Graph500 BFS has an extended historical past because the industry-standard benchmark as a result of it measures a system’s skill to navigate this irregularity at scale.
BFS measures the pace of traversing the graph via each vertex and edge. A excessive TEPS rating for BFS — measuring how briskly the system can course of these edges — proves the system has superior interconnects, comparable to cables or switches between compute nodes, in addition to extra reminiscence bandwidth and software program in a position to reap the benefits of the system’s capabilities. It validates the engineering of the whole system, not simply the pace of the CPU or GPU.
Successfully, it’s a measure of how briskly a system can “assume” and affiliate disparate items of data.
Present Methods for Processing Graphs
GPUs are recognized for accelerating dense workloads like AI coaching. Till not too long ago, the biggest sparse linear algebra and graph workloads have remained the area of conventional CPU architectures.
To course of graphs, CPUs transfer graph information throughout compute nodes. Because the graph scales to trillions of edges, this fixed motion creates bottlenecks and jams communications.
Builders use quite a lot of software program methods to avoid this difficulty. A standard method is to course of the graph the place it’s with lively messages, the place builders ship messages that may course of graph information in place. The messages are smaller and might be grouped collectively to maximise community effectivity.
Whereas this software program method considerably accelerates processing, lively messaging was designed to run on CPUs and is inherently restricted by the throughput fee and compute capabilities of CPU programs.
Reengineering Graph Processing for the GPU
To hurry up the BFS run, NVIDIA engineered a full-stack, GPU-only answer that reimagines how information strikes throughout the community.
A customized software program framework developed utilizing InfiniBand GPUDirect Async (IBGDA) and the NVSHMEM parallel programming interface permits GPU-to-GPU lively messages.
With IBGDA, the GPU can straight talk with the InfiniBand community interface card. Message aggregation has been engineered from the bottom as much as help lots of of hundreds of GPU threads sending lively messages concurrently, in contrast with simply lots of of threads on a CPU.
As such, on this redesigned system, lively messaging runs utterly on GPUs, bypassing the CPU.
This allows taking full benefit of the large parallelism and reminiscence bandwidth of NVIDIA H100 GPUs to ship messages, transfer them throughout the community and course of them on the receiver.
Working on the secure, high-performance infrastructure of NVIDIA companion CoreWeave, this orchestration enabled doubling the efficiency of comparable runs whereas utilizing a fraction of the {hardware} — at a fraction of the fee.
Accelerating New Workloads
This breakthrough has large implications for high-performance computing. HPC fields like fluid dynamics and climate forecasting depend on related sparse information constructions and communication patterns that energy the graphs that underpin social networks and cybersecurity.
For many years, these fields have been tethered to CPUs on the largest scales, at the same time as information scales from billions to trillions of edges. NVIDIA’s profitable outcome on Graph500, alongside two different prime 10 entries, validates a brand new method for high-performance computing at scale.
With the full-stack orchestration of NVIDIA computing, networking and software program, builders can now use applied sciences like NVSHMEM and IBGDA to effectively scale their largest HPC functions, bringing supercomputing efficiency to commercially obtainable infrastructure.
Keep updated on the newest Graph500 benchmarks and study extra about NVIDIA networking applied sciences.









